

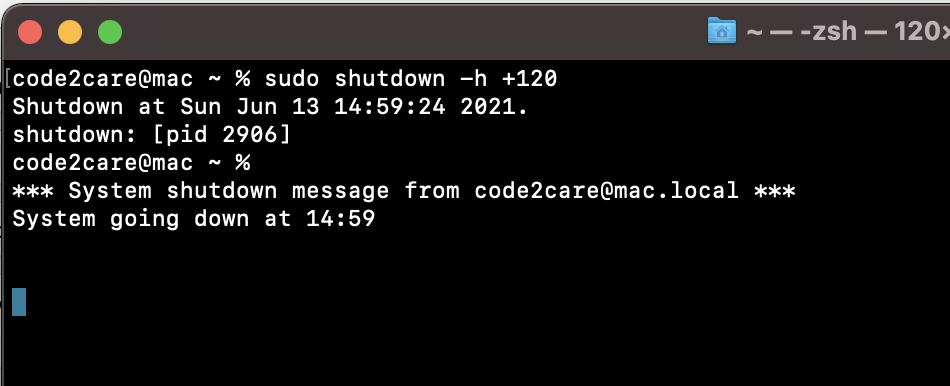
- #Mac shutdown from command line code#
- #Mac shutdown from command line password#
- #Mac shutdown from command line mac#
You can also launch Apple Diagnostics from the internet by holding Option+D at startup, which is handy if you can't get online.Ĭhris Hoffman is the former Editor-in-Chief of How-To Geek.
#Mac shutdown from command line mac#
Run Apple Diagnostics to check your Mac for known issues, then cross-reference any error codes you get with Apple Support. This includes USB drives that are plugged in while your computer starts up, Windows partitions created with Boot Camp, or additional macOS installs that are stored on external drives. If you want to boot from a different partition or volume then hold Option while your Mac boots to see a list of eligible boot disks. This allows you to do things like reinstall macOS, access Disk Utility to attempt to repair any drives, execute commands using the Terminal, or restore from a Time Machine backup. To access Recovery Mode, press and hold Command+R while your Mac boots. Some older Mac models may notice that some things like accelerated graphics, wireless networking, sharing, and more won't work while in Safe Mode. Assuming this volume is labeled "Macintosh HD" you can get there by typing: You'll find your drive under the "Volumes" directory. You can now perform similar operations on your startup drive using the command line as you could in good old single-user mode. Now quit Disk Utility and choose Terminal from the Utilities drop-down menu.
#Mac shutdown from command line password#
Use the "Mount" button and enter your password if prompted. If it's not, launch Disk Utility and click on your startup volume (probably "Macintosh HD"). When you log in to an admin account on Recovery Mode startup, your main startup disk should be mounted.
Though Apple Silicon doesn't have anything quite the same, you can access everything through Terminal in Recovery Mode. Single-user mode is a mode on Intel-based Macs that loads only the bare minimum services and extensions and dumps you in front of a command line. You can then choose whether to repeat the rest, restart, or shut down your Mac.
#Mac shutdown from command line code#
The start command can be used to start a stopped virtual machine or to resume a paused virtual machine.The troubleshooter will run and may give you a reference code to check on Apple's website for more information. The reset command first performs a 'hard' virtual machine shutdown and then starts it again. The restart command first gracefully shuts down a virtual machine and then starts it again. Depending on the ACPI support availability in the guest operating system, this may work or not. If the Parallels Tools package is not installed, the command will try to perform a graceful shutdown using ACPI.If the Parallels Tools package is installed in a virtual machine, the graceful shutdown will be performed using its facilities.If the parameter is omitted, the outcome of the graceful shutdown attempt will depend on the following: If the -kill parameter is included, the 'hard' shutdown will be performed. The stop command can perform a 'hard' or a graceful virtual machine shutdown. If this option is omitted, an attempt to perform a graceful shutdown will be made.

Perform a 'hard' virtual machine shutdown. The name of the virtual machine to start, stop, restart, reset, or check the status of. The ID of the virtual machine to start, stop, restart, reset, or check the status of. Start, stop, reset, and check the status of a virtual machine. Prlctl start, stop, restart, reset, status


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
